Enemas or suppositories
Enemas and/or suppositories can help people who have an upper motor neurone (UMN) ‘reflexic’ type-bowel and are unable to complete bowel elimination independently. The enema and/or suppository help to empty the rectum by providing stimulation and triggering the reflex to empty the rectum, when the sphincters are relaxed.
Please consider the person’s individual needs when planning any bowel procedures. Additional considerations may include previous personal experiences, education provided on the procedure and the person’s sensation or ability to feel the procedure.
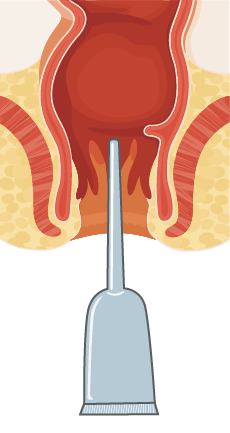
Enema in contact with the bowel wall.
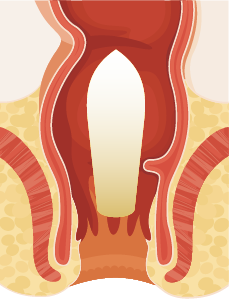
Suppository in contact with a bowel wall.
Procedure of inserting enemas or suppositories
Preparation
- Ensure a medication order is present.
- Prepare and set out the required equipment in advance:
- Non-sterile gloves
- Apron
- Water-based lubricant
- Protective pad (commonly known as a ‘Bluey’), if required
- Soap and water/wipes (for in bed)
- Plastic bag/bin available (for rubbish disposal)
- Ensure the individual’s dignity and privacy always are maintained at all times.
- Person administering the enema or suppository should introduce themselves, check the person’s identification, explain the procedure and obtain the person’s verbal consent. (Make it clear that the person can request to stop the procedure immediately, if they wish).
- If unstable injury:
- Procedure needs to take place during formal ‘log roll’ procedure.
- Ensure that correct positioning of the person, such as spinal alignment, is always maintained.
- If stable SCI:
- Procedure can take place in bed.
- Place the person in the left lateral position (if possible), flexing the knees to promote stability and expose the anus.
- If procedure is taking place in a shower commode:
- Position for comfort and anal access.
- Consider additional needs for safety, such as positioning to ensure anal skin is not stretched during the procedure, using a chest strap in situ and/or using a tilt on the commode chair.
- If known to suffer discomfort or signs/symptoms of AD
- Local anaesthetic gel may be instilled into rectum 10 minutes prior to procedure.
- Place protective pad, if required, on the bed or floor of bathroom. Enemas can be given over the toilet, if there is adequate access.
- Wear a plastic apron, wash hands and put on a pair of non-sterile gloves.
- Observe individual throughout procedure (especially those at risk of autonomic dysreflexia (AD)).
- Generously lubricate index finger with water-based lubricant.
Procedure
- Inform the person that the procedure is about to begin, then slowly and gently insert a single lubricated, gloved finger into the rectum (performing a digital check for faeces).
- Remove any faecal matter, if required, and dispose of gloves. Re-apply a new pair of clean gloves.
- If a suppository is used, this is inserted with the person lying on their side, on the bed. Some suppositories require time to melt and become effective. The person can be transferred to the toilet or commode when the suppository has had time to melt, prior to a bowel movement commencing. A protective bed pad may be required for the transfer, for protection. Please see more information in the Right time section, for selecting suppositories.
- If an enema is being used, this can be inserted with the person lying on the bed or sitting on the toilet/commode. Enemas have a shorter response time, so timing should be a consideration when deciding between a suppository or an enema. (See Right time for further guidance).
- Generously lubricate the suppository.
- Gently insert fingertip into the rectum, then insert the suppository into the rectum approximately 4cm (up to the second finger joint), ensuring contact against the mucosal wall.
- If using an enema, remove the top, lubricate the length of the administration tube and slide enema into the rectum, ensuring it is administered close to the mucosal wall. Ensure that the full length of the administration tube is inserted.
- Move the enema in a circular motion, to provide additional stimulation. When removing the enema, keep squeezing the tube until the nozzle is completely removed, to avoid vacuuming the contents back into the tube.
- Dispose of faecal matter in an appropriate receptacle.
- Remove gloves and apron, discard accordingly and perform hand hygiene.
- Apply non-sterile gloves to clean and dry person’s buttocks and anal area.
- Reposition the person, if required, and perform hand hygiene
- Record the outcome, such as the amount and consistency of stool (as per Bristol Stool Scale). See Right consistency for further guidance.
- Report any abnormalities to the person, team leader or medical officer and document accordingly.
Accessing enemas and suppositories in the community of inserting enemas or suppositories
Enemas and suppositories can be purchased from a pharmacy or a continence product company. A person may be eligible for some reduction in price with a prescription from a doctor (see Information for GP scripting) when these items are purchased at a pharmacy.
There are several types of government funding available t help cover medication costs, following an SCI. The type of funding utilised will influence the pathway options to access enemas and suppositories in the community. For more information, refer to the funding sources chart, below, or contact the relevant funding co-ordinator.
| Funding source | Explanation |
|---|---|
| National Disability Insurance Scheme (NDIS) | Enemas/suppositories are considered a medication by the NDIS, hence they are not funded. If enemas or suppositories are purchased on the continence account, the person may be asked to reimburse the cost price if they are audited by the NDIS. |
| National Injury Insurance Scheme (NIISQ) or a similar state scheme (e.g, iCare) | NIISQ may fund the cost of enemas/suppositories as part of the person’s injury management.These can be added to the continence product list (with a 3-month supply provided in bulk), or the person can obtain them through their NIISQ-funded pharmacy account.Any reductions in pricing (e.g. from a GP’s prescription) should be utilised to decrease the cost to NIISQ. |
| My Aged Care (MAC) | There is no specific funding provided. The person will need to purchase their enemas/suppositories either at the pharmacy or through a continence product company. |
| Department of Veterans Affairs (DVA) | Depending on their individual circumstances, prescriptions for enemas/suppositories may be available through the GP under the Repatriation Benefit Scheme. |
Prescription for enemas and suppositories
Most types of enemas and/or suppositories used in SCI bowel management can be bought over the counter, without a script, as they are not scheduled medications.
However, to access contributions towards the cost of enemas and/or suppositories a GP can provide a prescription subsidised by the Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme (PBS), as a Restricted Benefit.
- If the person has a Pensioner Concession Card or Health Care Card, the prescription will reduce the price to standard PBS medication prices (which can provide significant savings).
- If the person does not hold a Pensioner Concession or Health Care Card, the prescription may not significantly reduce the price of the enemas and/or suppositories, but it will contribute towards the person’s PBS Safety Net.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Micolette | The current brand of enema available through the PBS for prescription is Micolette. This is the equivalent of Microlax enemas which are readily available on pharmacy shelves. |
| Bisalax | The person can also get prescriptions for Bisalax enemas and suppositories. The subsidy for Bisacodyl enemas (e.g Bisalax) was discontinued in 2024. These may still be purchased over the counter at retail pricing only (e.g Bisalax, Toilax). |
Information for GP scripting
To access key PBS-subsidised enemas or suppositories, please prescribe:
Micolette enemas
| Name | CITRIC ACID + LAURYL SULFOACETATE SODIUM + SORBITOL |
| Dosage | Sodium citrate dihydrate 450mg/5ml + lauryl sulfoacetate sodium 45mg/5ml + sorbitol 3.123g/5ml enema, 12 x 5ml |
| Restricted benefit | 2091C Maximum 2 boxes 2 repeats |
| Clinical criteria | Paraplegic or Quadriplegic or Have severe neurogenic impairment of bowel function |
| Restricted benefit | 145349Y Maximum 4 boxes, 2 repeats |
| Clinical criteria | The condition must be stable for the prescriber to consider the listed maximum quantity of this medication suitable for this person AND must have paraplegia or quadriplegia with severe neurologic impairment of the bowel |
Bisalax enemas
| Name | BISACODYL |
| Dosage | Bisacodyl 10mg/5ml enema: 25 x 5ml 1 box 2 repeats |
| Restricted benefit | 1263L |
| Clinical criteria | Paraplegic or Quadriplegic or Have severe neurogenic impairment of bowel function |
Petrus bisacodyl suppositories
| Name | BISACODYL |
| Dosage | Bisacodyl 10mg suppository, 12 in a box |
| Restricted benefit | 1258F Maximum 3 boxes, 4 repeats |
| Clinical criteria | Paraplegic or Quadriplegic or Have severe neurogenic impairment of bowel function |
| Restricted benefit | 14305X Maximum 6 boxes, 4 repeats |
| Clinical criteria | The condition must be stable for the prescriber to consider the listed maximum quantity of this medication suitable for this person AND must have paraplegia or quadriplegia with severe neurologic impairment of the bowel |